Melanoma Skin Cancer
Dr. Beal is a melanoma expert who successfully treated over 200 melanomas last year. He is also leading the development of the largest head and neck melanoma research database in the United States.
What is Melanoma?
Melanoma is the third most common type of skin cancer. There are over 200,000 new cases of melanoma diagnosed annually.
Melanoma is due to the abnormal growth of melanocytes. Melanocytes are the skin cells that produce moles as well as pigment. 50% of melanomas begin as moles and 50% being in skin that appears normal.
Melanoma is the deadliest skin cancer. 75% of skin cancer related deaths are due to melanoma. This is because invasive melanomas can spread (metastasize). The ability of a melanoma to spread is directly related to its depth or thickness. Deeper melanomas (> 1mm thick) are more likely to spread beyond the skin to other organs. This is why early detection of melanoma is so important. Board-Certified Dermatologists are the experts for the diagnosis and treatment melanoma. Treatment success is directly related to the depth of the melanoma. Thankfully when melanoma is detected early, the 5-year survival rate is 98% in the United States.
Melanoma Symptoms (What does melanoma look like?):
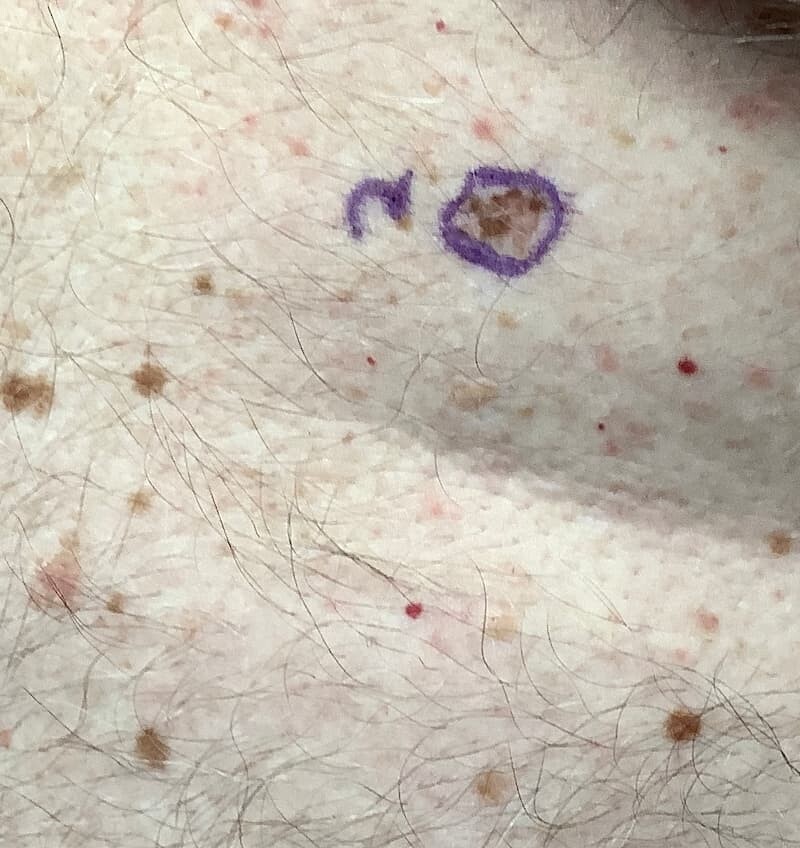
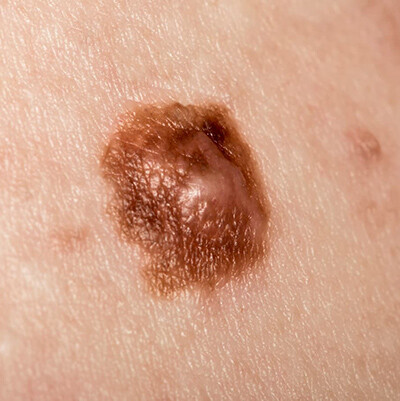
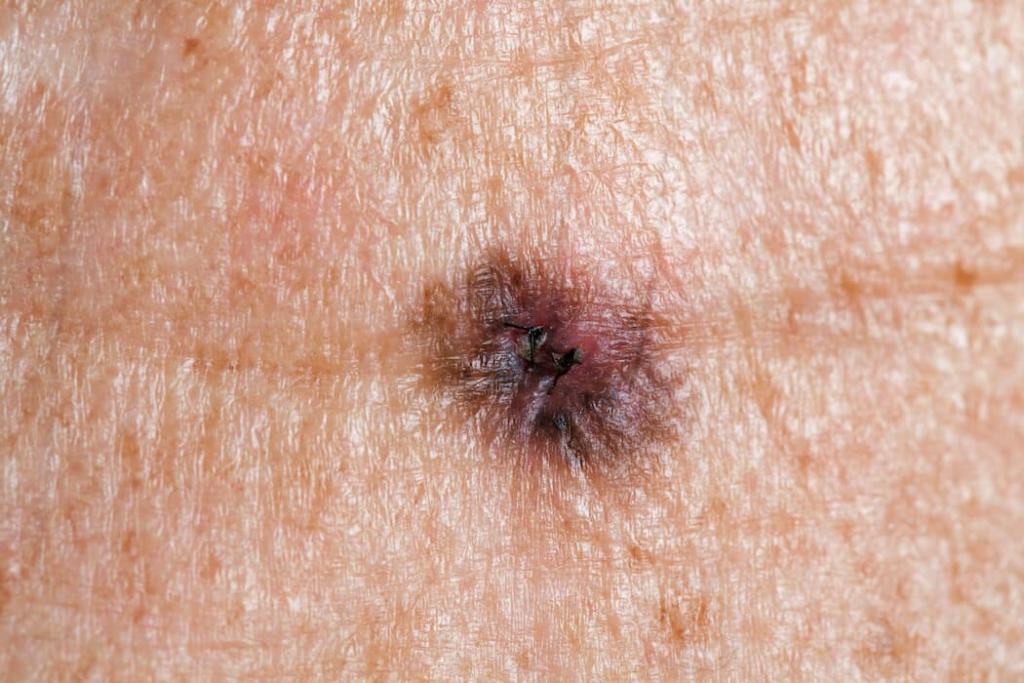
Melanoma often looks like a brown spot or mole that has changed:
- Grown larger (wider or thicker)
- Ulcerated/bleeds easier than your other moles
- Changed color (ex. become darker)
Melanomas can occur anywhere on the skin. In women, melanoma most commonly occurs on the legs and arms. In men, melanomas are more common on the trunk. As we age, melanomas become more common on our face and the sun exposed areas of our body.
The ABCDEs of melanoma are very important to help you identify melanoma early.
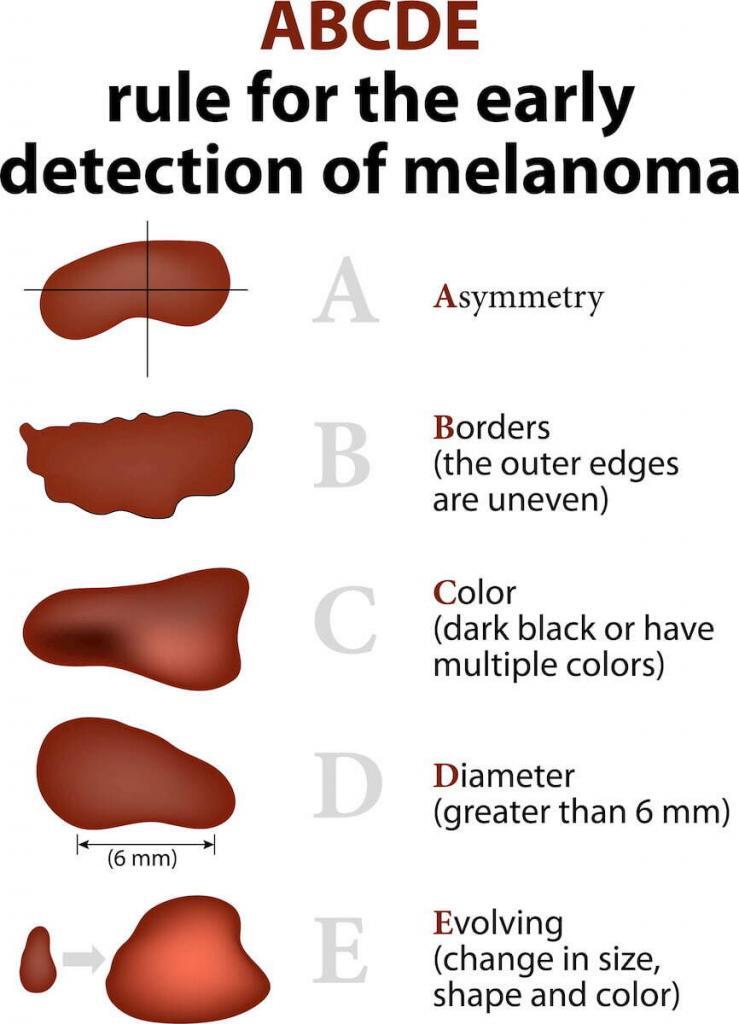
A = Asymmetry: is the mole symmetric, one side matches the other
B = Boarder irregularity: are the boarders regular/smooth (reassuring) or jagged and irregular
C = Color: does the mole or brown spot have the same color (reassuring) or many different colors (brown, blue, black, white or red)
D = Diameter: is the mole the size of a pencil eraser or smaller (<6mm)
E = Evolution: this is The Most Important. Is the mole changing? If your mole has changed you should schedule an appointment with a dermatologist.
Melanomas, like all skin cancers, can vary in appearance. There is no substitute for your skin concern being examined in-person by a Board-Certified Dermatologist. This is the gold standard for having any of your skin concerns addressed. Your Board-Certified Dermatologist will perform a comprehensive examination and is the expert when it comes to diagnosis and treating skin cancers.
The most common areas people forget to check for melanoma:
When examining your skin be sure to check:
- Scalp – it can be hard if you have lots of hair so ask a friend or your hairdresser
- Bottoms of your feet and in-between your toes
- Back and the back of your legs – Tip: use a full-length mirror and hand mirror
How to take high-quality photos with your phone:
- Make sure you are in a well-lit room with lots of light. Natural light is the best.
- Take your time and make sure the photos are in-focus. When you zoom in, the photos should still be clear and not blurry. If the photo is blurry when you zoom in, then camera did not focus on the correct area.
- First, take photos of an entire area. Ex. Left upper back, left lower back, right upper back, right lower back, left upper arm, left lower arm etc.
- Second, take a closeup photo of the concerning spot. We recommend closeup photos being taken with your camera 1 foot away from the lesion. A common mistake is to have the camera too close to the spot of concern.
- After you take these photos. Look at them and zoom in to make sure the photos are not blurry.
Risk factors for melanoma?
- Sun exposure without sun protection
- Having 2 or more severe/blistering sun burns
- Tanning beds or sunlamps
- Genetics – if you have a family member with melanoma you are at a higher risk of developing a melanoma
- Having greater than 50 moles
Melanoma Facts:
- Melanoma is the most common cancer for ages 25-29
- Greater than 50% of melanomas do not come from pre-existing moles. Said a different way, 50% of melanomas develop from seemingly normal skin.
- The FDA has categorized indoor tanning as a human carcinogen, meaning tanning beds cause cancer in humans.
- You can use your smartphone to take photos of your skin to document your moles, both how they look and their location. Then, if in the future you are concerned a spot changed, you can refer back to those high-quality photos.
How is melanoma diagnosed?
Melanoma is diagnosed with a skin biopsy. A skin biopsy is a minor procedure where your dermatologist will numb the area, and then take a sample of your lesion. This sample is examined microscopically for skin cancer cells. If skin cancer cells are seen, further treatment is required.
What is the best treatment for melanoma?
The best treatment for melanoma depends on several factors including:
- Depth or thickness of the melanoma
- Type of melanoma
- Location of the melanoma
- Your health & medical conditions
Melanoma can be a scary diagnosis and so it is important for you to discuss this diagnosis with an expert:

Brandon T. Beal, MD is a melanoma expert who successfully treated over 200 melanomas last year. He is also leading the development of the largest melanoma research database in the United States to help improve outcomes for patients with melanoma.
Dr. Beal provides each patient comprehensive counseling on the diagnosis and treatment of melanoma, a thorough skin examination from head to toe, and an individualized treatment plan based on evidenced-based medicine. Dr. Beal is an expert in Micrographic Surgery (Mohs Surgery) for melanoma which is the treatment that provides the highest cure rates and lowest local recurrence rates for head and neck melanoma. He follows the National Comprehensive Cancer Network Guidelines as well as the American Joint Committee on Cancer staging guidelines.
Dr. Beal completed a fellowship in Mohs Micrographic Surgery, Dermatologic Oncology, and Facial Reconstructive Surgery with a focus on the comprehensive diagnosis and treatment of melanoma. He also received training at the Cleveland Clinic’s Melanoma program, a multidisciplinary team of dermatopathologists, pathologists, dermatologists, and surgical, medical, and radiation oncologists.
More about Mohs Micrographic Surgery:
Mohs Micrographic Surgery is the treatment that offers the highest surgical cure rate amongst all treatments for head and neck melanomas. Mohs surgery is a technique that preserves your normal skin, focusing on removing the melanoma, and thereby minimizing scarring and maximizing your cosmetic outcome. Mohs Micrographic surgery is the most advanced treatment for head and neck melanoma.
Mohs Micrographic surgery examines 100% of the margin (edges) of the specimen that is removed. Meaning, 100% of the side and bottom edges of the specimen are examined microscopically to ensure there are no melanoma cells at the edges. Mohs Micrographic surgery provides patients the highest cure rates, smallest scars, and best cosmetic outcomes.
The treatment of your melanoma with Mohs Micrographic Surgery and immunohistochemical stains as well as the reconstruction are performed and completed during the same day at our office. The procedure is done under local anesthesia which provides increased safety and comfort to our patients.